WFI Engineering Model Passes Stray Light Test
The PUNCH mission consists of four spacecraft in Earth orbit that together will be uniquely capable of imaging the space environment from the outer corona of the Sun all the way to Earth orbit. There is a Near Field Imager and three Wide Field Imagers (WFIs).
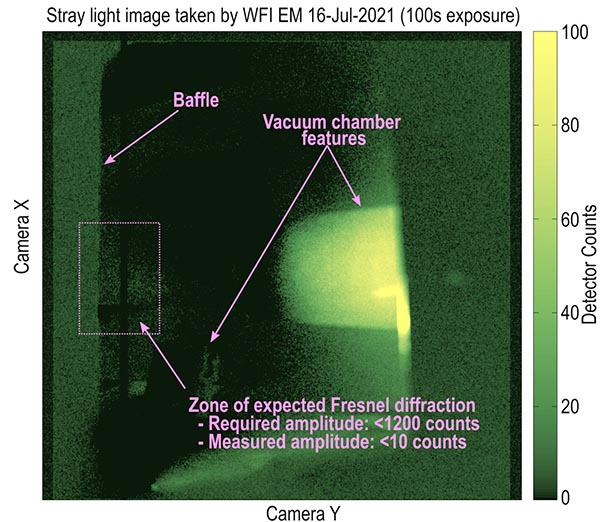
The complete Engineering Model WFI has been undergoing qualification tests at SwRI and at NRL. The most arduous is the baffle stray light test, which ensures that the end-to-end system meet its requirement to attenuate incoming sunlight by 16 orders of magnitude.
WFI’s attenuation coefficient is at most 10-18, giving a margin of at least 100x compared to instrument requirements.
This result reveals that, as built, WFI is sufficiently sensitive to carry out our wide-field science.
Thanks to Glenn Laurent, Derek Lamb, Michael Shoffner, and Steve Osterman (the PUNCH Away Team) for preparing and testing WFI through this important milestone, and to Robin Colaninno, Don McMullin, and the SCOTCH support team for enabling this key test.
NFI and the flight WFIs are scheduled to be tested at SCOTCH in about a year’s time.